… at the Center for Biological Data Science at Virginia Commonwealth University
The Uetz lab is working on proteins, protein function, bioinformatics and reptile taxonomy. Some of our recent projects and publications include:
 Reptile taxonomy and biodiversity informatics. There are not only millions of proteins but also millions of species. Our contribution to biodiversity research is the Reptile Database, taxonomic data analysis, and its integration with other data sources:
Reptile taxonomy and biodiversity informatics. There are not only millions of proteins but also millions of species. Our contribution to biodiversity research is the Reptile Database, taxonomic data analysis, and its integration with other data sources:
- Chapple, D. et al. 2021. Conservation Status of the World’s Skinks (Scincidae) […]. Biological Conservation 257: 109101.
- Garg, A. et al. (2019) DNA and species names in the NCBI taxonomy database. Zootaxa 4706 (3): 401–407
- Roll U et al. (2017) Global distribution of tetrapods and reptile conservation. Nature Ecol. Evol. 1: 1677–1682
- Castoe, T. A. et al. (2013) The Burmese python genome. PNAS, Dec 2, 2013.
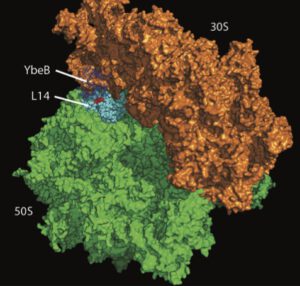 Protein function, protein complexes, and protein domains. We study protein function, especially of uncharacterized and poorly understood proteins using both computational and experimental approaches. Our group has solved the function of half a dozen uncharacterized proteins and domains:
Protein function, protein complexes, and protein domains. We study protein function, especially of uncharacterized and poorly understood proteins using both computational and experimental approaches. Our group has solved the function of half a dozen uncharacterized proteins and domains:
- Mehla, J. et al. (2021) ZapG (YhcB/DUF1043), a novel cell division protein […] J Biol. Chem. 296:100700
- Goodacre, N.F. et al. (2014) Protein domains of unknown function are essential in bacteria. mBio 5 (1): e00744-13.
- Häuser, R. et al. (2012) RsfA (YbeB) proteins are ribosomal silencing factors. Plos Genetics 8(7): e1002815.
Microbial interactomics. Our group has mapped the interactomes of 5 different microbes, more than any other lab in the world. These interactomes provide insights into the molecular organization of cells and protein function:
- Streptococcus pneumoniae / Meta-interactomes. Wuchty, S et al. (2017) mSystems 2(3): e00019-17
- Escherichia coli: Rajagopala, SV et al. (2014) Nature Biotechnology, 32, 285–290
- Helicobacter pylori: Häuser, R. et al. (2014) Mol Cell Proteomics 13(5):1318-29
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Uetz, P. et al. (2000) Nature 403: 623-627
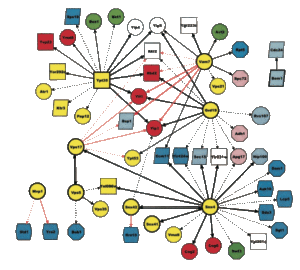 Bioinformatics of protein networks. We also analyze the networks we have produced experimentally with a variety of bioinformatics methods. We strive to understand complex networks but also individual proteins and protein domains (see Protein function … below):
Bioinformatics of protein networks. We also analyze the networks we have produced experimentally with a variety of bioinformatics methods. We strive to understand complex networks but also individual proteins and protein domains (see Protein function … below):
- Mariano R. et al. (2016) Infection Patterns of Human Viruses and Bacteriophages. mSystems 1 (2): e00030-15.
- Uetz, P. et al. (2006) Herpesviral Protein Networks and the Human Proteome. Science 311: 239-242
- Schwikowski, B. et al. (2000) A network of interacting proteins in yeast. Nature Biotech. 18 (12): 1257-1261
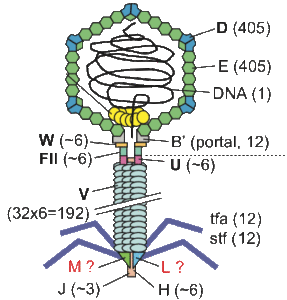 Virus and phage interactomics. Viruses and phage are excellent models to study protein interaction networks and protein function because they are small and have loads of uncharacterized proteins. We have studied both human viruses and phage of various bacteria, including E. coli, Mycobacteria, and Streptococcus:
Virus and phage interactomics. Viruses and phage are excellent models to study protein interaction networks and protein function because they are small and have loads of uncharacterized proteins. We have studied both human viruses and phage of various bacteria, including E. coli, Mycobacteria, and Streptococcus:
- Osterman A. et al. (2015) The Hepatitis E virus intraviral interactome. Scientific Reports 5: 13872.
- Blasche S. et al. (2013) Interactions of Bacteriophage Lambda with E. coli. J Virol. 87 (23): 12745-55
- Häuser, R. et al. (2011) The interactome of Streptococcus pneumoniae phage Cp1. J. Bact. 193 (12): 3135–3138.
- Fossum E. et al. (2009) Herpesviral protein interaction networks. PloS Pathogens 5 (9): 00570
See also Lab Members